🐍 Data Post-processing
The Post-processing step allows you to modify parsed data before exporting it to webhooks, Zapier etc. Write Python code to add custom formatting and business logic: merge or split fields, format dates, prevent some documents from being exported and much more.
Some popular use cases:
Normalize fields format, reformatting dates or numbers.
Format data to make an API call without passing by an automated platform (Zapier/Make/Pabbly Connect etc.).
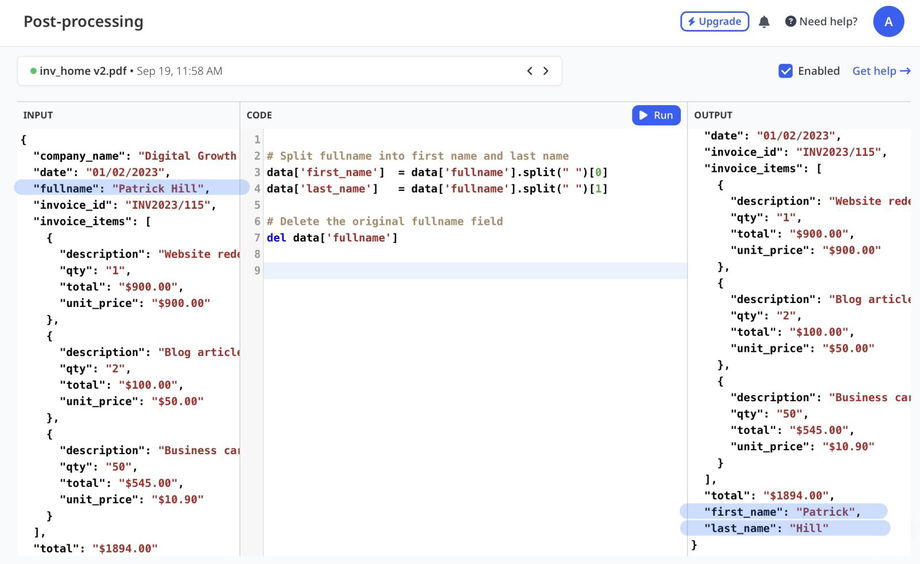
Create, modify, split, merge or remove some fields.
Add additional business logic.
Avoid exporting some documents based on certain condition.
Post-processing is completely optional. It’s an extra step that lets you modify or reshape the parsed data after Airparser extracts it and before it’s sent to integrations (Zapier, Make, webhooks, etc.).
If you don’t have any special formatting needs, you can safely ignore post-processing.
Before writing the Python code, it's important to have a basic knowledge of Python and its syntax in order to use this feature efficiently. If you need any help, please don't hesitate to contact our support
Writing Python Code
The parsed data is stored in the data dictionary.
Available Python libraries
The following Python libraries are available (you don't need to import them):
Regular expression operations. | |
Module provides support for fast correctly rounded decimal floating point arithmetic. | |
Module supplies classes for manipulating dates and times. |
Python built-in functions
Many Python built-in functions are supported. Here are some of the most useful functions:
| Returns a string object |
| Returns an integer number |
| Returns a floating point number |
| Returns a sequence of numbers, starting from 0 and increments by 1 (by default) |
| Returns the length of an object |
| Returns the absolute value of a number |
| Returns the largest item in an iterable |
| Returns the smallest item in an iterable |
| Returns the value of x to the power of y |
| Construct an iterator from those elements of iterable for which function returns true. |
| An analog of json.loads() that parses a JSON string and returns a Python dictionary. |
| An analog of json.dumps() that converts a Python dictionary into a JSON-formatted string. |
Please refer to the official documentation to learn more.
Python string methods
Here are some of the most useful string methods:
| Converts a string into upper case |
| Converts a string into lower case |
| Converts the first character to upper case |
| Returns true if the string ends with the specified value |
| Returns true if the string starts with the specified value |
| Removes spaces at the beginning and at the end of the string |
| Converts the first character of each word to upper case |
| Swaps cases, lower case becomes upper case and vice versa |
| Splits the string at the specified separator, and returns a list |
| Returns a string where a specified value is replaced with a specified value |
| Returns True if all characters in the string are digits |
| Returns True if all characters in the string are in the alphabet |
| Returns True if all characters in the string are alphanumeric |
Please refer to the official documentation to learn more.
Limitations
For reasons of security and simplicity, we use a restricted version of Python. Here are some unsupported features:
import of additional Python packages
whileloopsprintfunctionvariables starting with underscore:
_foo = 42Python classes
Hotkeys
Our code editor supports the following hotkeys:
Ctrl+S: run and saveCtrl+/: comment outCtrl+X: delete lineTab,Shift+Tab: indent and outdentCtrl+Z,Ctrl+Shift+Z: undo and redoCtrl+F: search
Mac users: use the Cmd button instead of Ctrl.

